Generic Name: Bacitracin
Brand Names: Various around the world
What is Bacitracin?
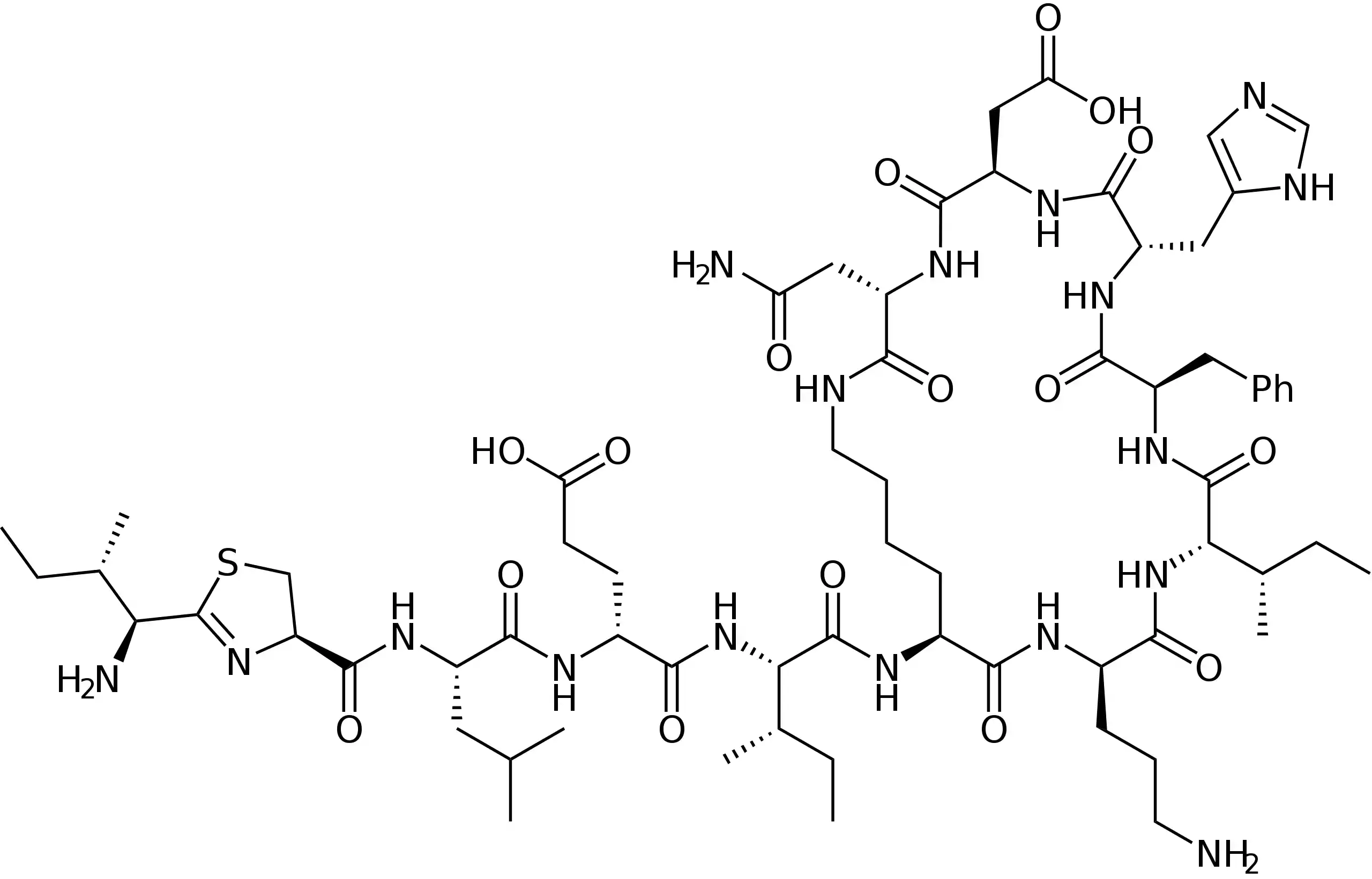
The antibiotic bacitracin is used to treat gram-positive bacterial infections. Drugs containing bacitracin are sometimes marketed under the names Baci-IM, Baciguent, Bakan, and Baxin. The bacterium Bacillus subtilis yielded bacitracin, which was initially identified in 1945 and utilised as an antibiotic in 1948. To comprehend the structure and mode of action of bacitratracin, we will examine publications such as “Bacitracin sensing in Bacillus subtilis” (Rietkötter et al., 2008), “Anatomy of the bacitracine resistance network in Bacillus subtilis” (Radeck and al., 2016), and “High-resolution crystal structure reveals molecular details of target recognition by bacitrazin” (Economou et al. 2013). A peptide antibiotic called bacitracin prevents bacteria from synthesising their cell walls.
Chemical Structure and Mechanism of Action
A fatty chain and twelve amino acids make up the cyclic polypeptide known as bacitracin. It is able to connect with the bacterial cell membrane because of its special structure. Bacitracin specifically binds to C55 isoprenyl pyrophosphate synthase, an enzyme that is involved in the formation of bacterial cell walls. The bacterial cell’s osmotic solution results from the deregulation of cell wall production caused by this protein interaction. Bacitracin’s distinct mode of action primarily targets gram-positive bacteria, while gram-negative bacteria are inherently resistant because of their outer membrane.
Uses
The principal application for bacitracin is as a topical medication for infections of the skin and mucous membranes brought on by gram-positive bacteria like Streptococcus and Staphylococcus. For application on the skin, eyes, nose, and ears, it comes in a variety of pharmaceutical formulations, including ointments, creams, and suspensions. Bacitracin can be used prophylactically to prevent postoperative infections following minor surgical procedures, in addition to treating infections. However, because of the possibility of toxicity and systemic absorption, it is not advised to be used on large open wounds.
Side Effects
Although it is generally safe when used topically, there is a chance of some negative effects. The most typical ones include rash, itching, skin irritation, and hypersensitivity responses. Pain, swelling, and exfoliation at the application site are uncommon adverse effects. Although it is uncommon, systemic absorption via topical use might result in neurotoxicity or renal failure. A study by Rietkötter et al. (2008) titled “Bacitracin sensing in Bacillus subtilis” describes how it stresses the bacteria’s cell walls, causing signals to be released and defensive systems to be activated.
Warnings
Large portions of the skin or open wounds should not be treated with Bacitracin due to the increased risk of toxicity and systemic absorption. Additionally, because there is a chance that the medication can accumulate in the body, using it in patients with renal failure is not advised. Extended usage could result in the emergence of resistant bacterial strains, thus it’s best to avoid it. Radeck et al. (2016) reported in their research “Anatomy of the bacitracin resistance network in Bacillus subtilis” that bacteria have evolved many defensive mechanisms to safeguard their cell wall against bacitraquin.
Precautions
When using Bacitracine, use caution and see a physician beforehand. It’s critical to strictly adhere to the medication’s usage recommendations and not to go above the suggested dosage or course of therapy. Severe adverse effects should be promptly reported and the use stopped. Economou et al. (2013) note in their paper “High-resolution crystal structure reveals molecular details of target recognition by bacitracin” that the selective action of bacitracin is caused by interactions with certain proteins in bacterial cell walls.
Contraindications
Those who have a history of recognised hypersensitivity to any of the preparation’s ingredients or to the medication itself should not take bacitracin. Its substantial risk of nephrotoxicity makes it inappropriate to administer it on a regular basis. Additionally, since it cannot be properly eliminated from the body, its usage is not advised in patients with severe renal failure. The dangers associated with continuous, long-term topical bacitracin use include the potential for resistant bacterial strains to emerge, as noted by Radeck et al. in their investigation. (2016).
Interactions
Drug interactions between bacitracin and other medications may modify the former’s own actions or the latter’s. For instance, using aminoglycosides like tambramycin or gentamicin concurrently may raise the risk of renal or neuromuscular damage. Tetracycline’s intestinal absorption may also be reduced by bacitracine. It’s efficacy may be impacted by Rietkötter et al. (2008)’s findings that it triggers resistance systems and other defensive mechanisms in bacteria.
Overdose
Although it’s systemic absorption following topical administration is uncommon, an overdose can have major negative effects. Overdosing can cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, renal failure, and problems of the neuromuscular system. According to Economou et al. (2013), a high bacitracin concentration can cause bacterial cell disintegration by interfering with the cell wall’s normal function. Depending on the symptoms, prompt medical monitoring and supportive treatment measures are advised in the event of an overdose.
Summary
A peptide antibiotic called bacitracin is used to treat gram-positive bacterial local infections of the skin and mucous membranes. It prevents bacteria from synthesising their cell walls, which dissolves the germs. It may irritate skin or trigger hypersensitivity responses and is applied as an ointment, cream, or suspension. It’s usage has to be under medical supervision due to potential overdose hazards and medication interactions. Nephrotoxicity makes systemic administration contraindicated. Bacteria have evolved defensive mechanisms against bacitracin, and prolonged use of the drug may result in resistant strains. Following the directions, avoiding systematic administration, keeping an eye out for adverse effects, and limiting the length of therapy to prevent resistant strains are all fundamental aspects of using it safely.
ATTENTION: It is of vital importance to never take any medication without the supervision and guidance of a specialised doctor. Consult the package insert of each prescribed medicinal product, as each pharmaceutical company accurately describes the specific specifications for the product, which may undergo regular updates. Note that the trade names mentioned in this article correspond to well-known medicinal products that contain the active substances under analysis. However, there may be variations depending on the composition of each drug. This article focuses on the active substance analysis rather than the drug’s trade name. The reference to trade names is made exclusively for the convenience of readers, who should carefully study the instruction leaflet for each commercial preparation they use. It is necessary to have close cooperation with your attending physician and your pharmacist. The self-administration of any medication carries serious health risks and should be strictly avoided.
Bibliography
- Rietkötter, E., D. Hoyer, and T. Mascher. “Bacitracin sensing in Bacillus subtilis.” Molecular microbiology 68.3 (2008): 768-785.wiley
- Radeck, J., et al. “Anatomy of the bacitracin resistance network in Bacillus subtilis.” Molecular microbiology 100.4 (2016): 607-620. onlinelibrary
- Economou, N. J., et al. “High-resolution crystal structure reveals molecular details of target recognition by bacitracin.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 110.39 (2013): 14507-14512.pna