Generic Name: Baclofen
Brand Names: Various around the world
What is Baclofen;
Baclofen is a muscle relaxant and antispasmodic medication used to treat muscle spasms, pain, and stiffness caused by multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injuries, and other neurological disorders. Baclofen side effects will be extensively analysed later in the text. Some popular brand names containing baclofen include Lioresal, Liofen, Baclon, and Gablofen. Baclofen was first synthesized in 1962 by Heinrich Keberle at Ciba-Geigy, now known as Novartis, in Basel, Switzerland. In this article, we will analyse information from the journals “SAGE open” and “Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research,” as well as the book “Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface,” regarding baclofen’s therapeutic uses, toxicity, and withdrawal effects.
Chemical Structure and Mechanism of Action
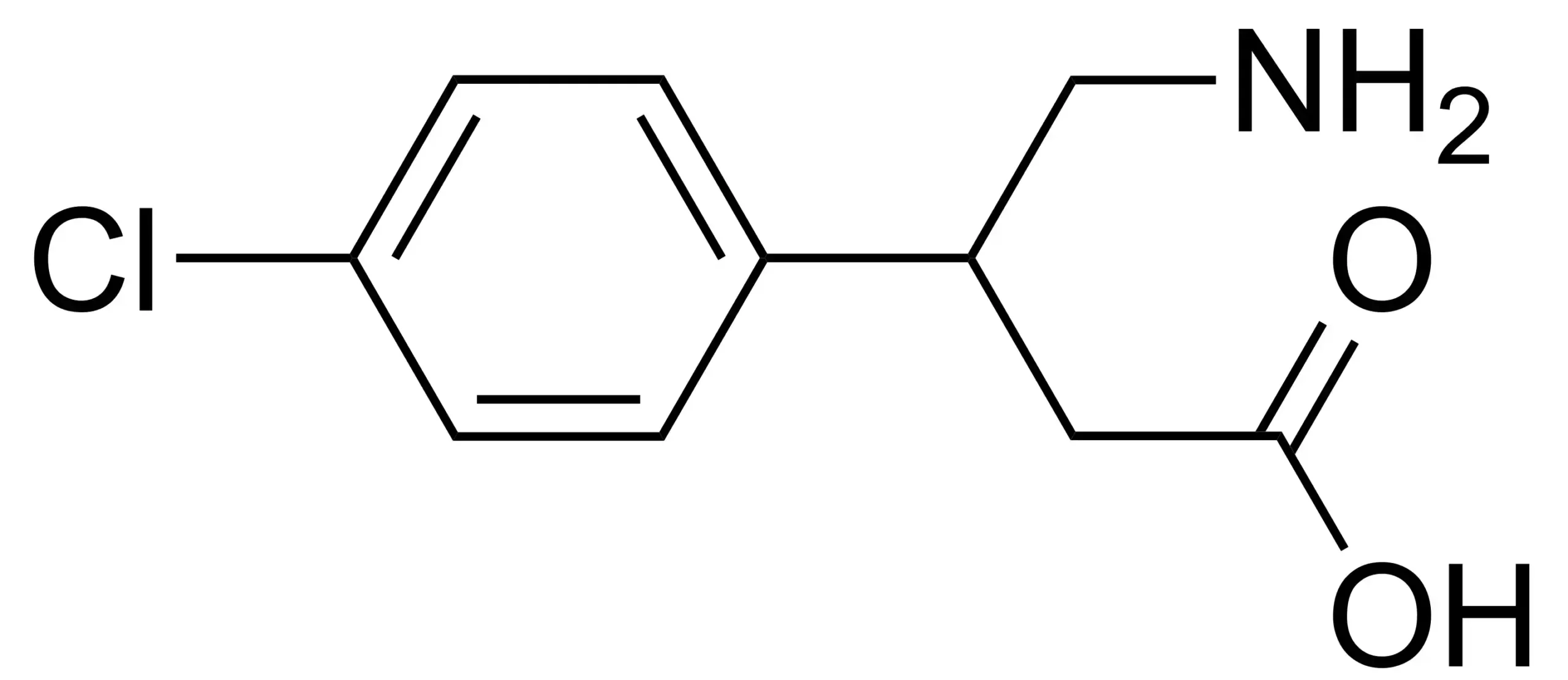
Belonging to the group of gamma-aminobutyric acid derivatives, baclofen is an agonist of the GABA-B receptors (GABA). β-(4-chlorophenyl)-GABA is its chemical name. By blocking the monosynaptic and polysynaptic reflex pathways, baclofen functions as an agonist of the spinal cord’s pre- and post-synaptic GABA-B receptors. This causes skeletal muscle relaxation and a decrease in muscular spasm due to a decrease in the release of stimulating neurotransmitters like glutamine and aspartame.
Uses
The primary purpose of baclofen is to treat spasticity brought on by neurological conditions such multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injuries, and cerebral palsy. Moreover, it can be utilised to treat generalised motor hypertension, dystonia, and chronic pain (Romito et al., 2021). Moreover, baclofen has been researched as a potential alcohol dependency therapy. Garbutt et al. (2010) discovered that baclofen dramatically decreased alcohol intake and desire for alcohol in individuals with alcohol dependency in a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled experiment. Nevertheless, more research is required to validate baclofen’s efficacy in this demographic. It’s crucial to speak with a physician to find out if baclofen is appropriate for your situation.
Baclofen Side Effects
Common Baclofen Side Effects
The most typical adverse effects of baclofen are nausea, vomiting, weakness, and sleepiness. Headaches, disorientation, exhaustion, and sleep disturbances might also happen. Certain patients may go through phases of exhilaration or despair. Constipation, diarrhoea, and dry mouth are other potential gastrointestinal side effects. Muscle weakness or cramps may be brought on by baclofen, particularly during the first few days of therapy or following dosage increases.
Rare But Possible Baclofen Side Effects
Shortness of breath, redness, and itching are examples of allergic responses that are less common adverse effects of baclofen. Vision problems can also happen, causing things like dyplopia or tripping. Baclofen may occasionally result in visual or auditory hallucinations. There have been cases of bradycardia, arrhythmias, and hypotension. Tremors, abnormalities, and hallucinations are uncommon neurological adverse effects.
Serious Baclofen Side Effects
Baclofen occasionally has major adverse effects that need to be treated right away by a doctor. These include severe allergic responses, including anaphylaxis, which can cause shock, facial or throat swelling, and breathing difficulties. Particularly in situations of overdose, serious neurological side effects, such as suppressive effects on the central nervous system, might result in respiratory suppression, coma, or even death (Romito et al., 2021). Seizures and periods of psychosis have also been reported. After long-term usage, abruptly stopping baclofen can cause withdrawal syndrome, which is characterised by bewilderment, convulsions, spasms, and possibly fatal consequences.
Warnings
Inform your doctor about any allergies or pre-existing medical illnesses, particularly kidney, liver, or psychological disorders, before starting baclofen. Patients with a history of seizures, thoughts of suicide, or substance abuse should use baclofen with care. Careful monitoring is necessary since older individuals may be more vulnerable to baclofen’s negative effects. Baclofen has been demonstrated to cross the placenta, hence pregnant women should only use it if the advantages outweigh the possible hazards to the foetus (Saulino et al., 2016). Breastfeeding is not advised when receiving baclofen since the medication may potentially be secreted in breast milk. Patients should abstain from tasks requiring alertness, such operating machinery or driving, until they have a better understanding of how the medication affects them.
Precautions
Patients with renal impairment should take baclofen with caution since increased risk of toxicity and drug accumulation can result from renal failure. Adjusting the dosage is necessary in these situations. Similarly, because baclofen is metabolised in the liver, individuals with hepatic impairment need to be properly watched. It is advised to gradually lower the dose of baclofen under medical supervision since abrupt termination of the medication after extended usage may result in withdrawal syndrome (Romito et al., 2021). Baclofen usage should be cautious in patients with a history of mental illnesses, such as depression or psychosis, since it may make these symptoms worse. It is best to avoid using baclofen concurrently with other medications that also depress the central nervous system, such as alcohol, benzodiazepines, or opioids, since this increases the risk of drowsiness and respiratory suppression.
Contraindications
Patients who have a history of known allergy to any of the drug’s derivatives should not use baclofen. Baclofen can reduce the frequency of seizures, thus those with current epilepsy or a history of seizures should not use it. Baclofen should not be used in individuals with purpurea since it may cause acute purple seizures. Patients who have recently developed or are currently experiencing gastrointestinal ulcers should use baclofen with caution as it may make their situation worse. Patients with severe hepatic or renal failure should not use baclofen since these factors might alter the drug’s pharmacokinetics and raise the possibility of adverse effects (Saulino et al., 2016). Baclofen should be used cautiously in individuals with severe respiratory failure since it can worsen respiratory suppression. Since baclofen has been associated with congenital malformations in animal studies, it is not recommended to be used during pregnancy unless the benefits to the foetus clearly exceed the dangers.
Interactions
Several medications may interact with baclofen, compromising its safety or efficacy. When baclofen is used in combination with other GABA-B receptor agonists like gabapentin or pregabalin, there may be a higher chance of adverse effects including fatigue, lightheadedness, and suppression of the respiratory system. The central nervous system suppressants baclofen, like benzodiazepines, opioids, antipsychotics, and antidepressants, can intensify baclofen’s suppressive effects (Romito et al., 2021). When baclofen is used alongside antihypertensive medications, the blood pressure may be drastically lowered. When used with batofen, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) may raise the risk of bleeding and stomach ulcers. Drug levels in the blood may fluctuate when baclofen interacts with medications that are broken down by the cytochrome P450 system in the liver, including certain antibiotics, antifungals, and antiepileptic medications.
Overdose
Overdosing on baclofen is a dangerous medical condition that can have potentially fatal consequences. According to Garbutt et al. (2010), signs and symptoms of an overdose include bradycardia, hypotension, sleepiness, lethargy, coma, respiratory suppression, and convulsions. Severe instances may result in cardiac arrhythmias, respiratory failure, and even death. The management of a baclofen overdose include supportive care, with a focus on respiratory and circulatory assistance as well as airway preservation. If swallowing has recently happened, stomach cleansing and the administration of activated charcoal may be useful. Clobofen removal from the body may need hemodialysis in people with renal failure. It is essential to closely evaluate renal function, electrolytes, and vital signs. In extreme situations, the use of medications like physostigmine can aid in the reversal of central nerve suppression. Keeping baclofen away from minors and other susceptible people, following dosage instructions, and refraining from taking many suppression medications at once are all important ways to prevent baclofen overdose.
Briefly
Muscle spasm and spasm related to neurological conditions such multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, and cerebral palsy are treated with the muscle relaxant baclofen. It functions as an agonist of GABA-B receptors, preventing nerve impulses from reaching the spinal cord. Although baclofen is usually well accepted, there are certain adverse effects that may occur, including weakness, sleepiness, and gastrointestinal issues. Withdrawal syndrome, allergic responses, and respiratory suppression are uncommon but potentially dangerous side effects. Patients with epilepsy, liver or renal disease, and mental health issues need to take precautions. Many medications, particularly those that inhibit the central nervous system, interact with baclofen. Overdosing on baclofen can result in fatal consequences such as respiratory failure, coma, and death. To maximise safety and efficacy when using baclofen, close physician care is required. Patients should notify their doctor of any concerning symptoms and be informed of the possible dangers and advantages of the treatment.
ATTENTION: It is of vital importance to never take any medication without the supervision and guidance of a specialised doctor. Consult the package insert of each prescribed medicinal product, as each pharmaceutical company accurately describes the specific specifications for the product, which may undergo regular updates. Note that the trade names mentioned in this article correspond to well-known medicinal products that contain the active substances under analysis. However, there may be variations depending on the composition of each drug. This article focuses on the active substance analysis rather than the drug’s trade name. The reference to trade names is made exclusively for the convenience of readers, who should carefully study the instruction leaflet for each commercial preparation they use. It is necessary to have close cooperation with your attending physician and your pharmacist. The self-administration of any medication carries serious health risks and should be strictly avoided.
Bibliography
- Romito, J. W., Turner, E. R., Rosener, J. A., & Barton, D. (2021). Baclofen therapeutics, toxicity, and withdrawal: a narrative review. SAGE Open Medicine, 9, 20503121211022197. journals.sagepub
- Garbutt, J. C., Kampov‐Polevoy, A. B., Gallop, R., Kalka‐Juhl, L., & Flannery, B. A. (2010). Efficacy and safety of baclofen for alcohol dependence: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 34(11), 1849-1857. onlinelibrary.wiley
- Saulino, M., Ivanhoe, C. B., McGuire, J. R., Ridley, B., Shilt, J. S., & Boster, A. L. (2016). Best practices for intrathecal baclofen therapy: patient selection. Neuromodulation: Technology at the Neural Interface, 19(6), 607-615. sciencedirect