Table of Contents
ToggleGeneric Name: Eberconazole
Brand Names: Various around the world
What is Eberconazole?
Eberconazole is an antifungal medication belonging to the imidazole class of drugs. Eberconazole side effects and uses will be extensively analysed later in the text. This broad-spectrum antifungal agent was first synthesised in the late 1980s and has since been widely employed in the treatment of various fungal infections, particularly those affecting the skin and mucous membranes. In this article, we shall examine research from the Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology, the American Journal of Otolaryngology, and Therapeutic Delivery, shedding light on the pharmacological properties, clinical applications, and potential side effects associated with eberconazole.
Chemical Structure and Mechanism of Action
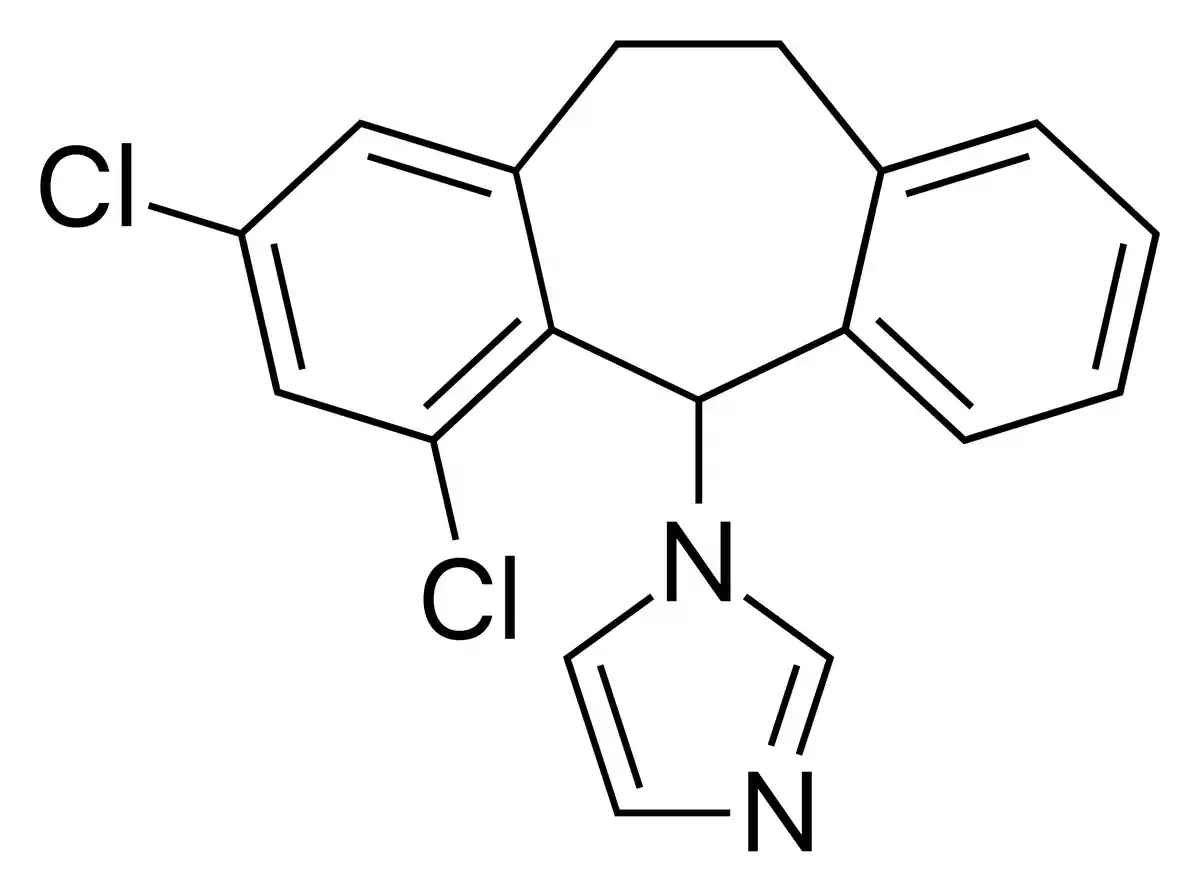
Eberconazole, chemically known as 1-[2,4-difluoro-α-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)benzyl]-1-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl]imidazole, is a synthetic imidazole derivative. It is made up of an imidazole ring in the middle, two triazole rings on either side, and a difluorophenyl moiety connected to one of the triazole rings. This unique molecular configuration confers eberconazole with its potent antifungal properties.
Eberconazole works by stopping the biosynthesis of ergosterol, which is an important part of the fungal cell membrane. Ergosterol plays a crucial role in maintaining the structural integrity and permeability of the fungal cell membrane. Eberconazole inhibits the enzyme lanosterol 14α-demethylase, which is responsible for a critical step in the ergosterol biosynthetic pathway. By disrupting this pathway, eberconazole depletes ergosterol levels within the fungal cell, leading to compromised cell membrane function and eventually, cell death.
Ergosterol biosynthesis is stopped by eberconazole, and it also works against many other types of pathogenic fungi, such as dermatophytes (like Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton species), yeasts (like Candida albicans), and other opportunistic fungi. This versatility makes eberconazole a valuable therapeutic option in the management of a wide range of superficial and mucocutaneous fungal infections.
Uses
Eberconazole is primarily employed as a topical antifungal agent for the treatment of various superficial and mucocutaneous fungal infections. It can help with dermatophyte infections (like tinea corporis, tinea cruris, tinea pedis, and tinea versicolor), candidiasis, and other fungal infections that happen when they can. These can affect the skin, nails, and mucous membranes.
Eberconazole Side Effects
While eberconazole is generally well-tolerated, like all medications, it may cause certain side effects in some individuals. It is essential to weigh the potential benefits against the risks and consult with a healthcare professional before using this antifungal agent.
Common Eberconazole Side Effects
The most commonly reported side effects associated with eberconazole are typically mild and localized. These may include:
- Skin irritation, redness, or rash at the application site
- Burning or stinging sensation
- Itching or dryness
Rare but Possible Eberconazole Side Effects
In rare cases, some individuals may experience the following side effects when using eberconazole:
- Allergic reactions (e.g., swelling, hives, difficulty breathing)
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Dizziness or vertigo
Serious Eberconazole Side Effects
While uncommon, certain serious side effects have been reported with the use of eberconazole. These include:
- Liver dysfunction or hepatotoxicity (as highlighted in the Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology article by Moodahadu-Bangera et al.)
- Severe skin reactions (e.g., blistering, peeling)
- Photosensitivity or increased sensitivity to sunlight
It is crucial to promptly report any concerning symptoms to a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and management.
Warnings
It is essential to exercise caution when using eberconazole and to follow all instructions provided by healthcare professionals or product labeling. Failure to adhere to proper usage guidelines may increase the risk of adverse effects or diminish the medication’s effectiveness.
- Eberconazole should not be used for prolonged periods without medical supervision, as extended use may increase the risk of adverse reactions or promote the development of resistant fungal strains.
- Avoid applying eberconazole to broken or irritated skin, as it may exacerbate irritation or lead to systemic absorption, potentially increasing the likelihood of side effects.
- Eberconazole should not be used in combination with other antifungal medications or products without consulting a healthcare professional, as drug interactions may occur, potentially altering the efficacy or safety profile.
Precautions
When using eberconazole, certain precautions should be taken to ensure safe and effective use:
- Inform healthcare providers about any existing medical conditions, allergies, or medications being taken, as eberconazole may interact with certain drugs or exacerbate certain conditions.
- Avoid direct contact with eyes, ears, or mucous membranes unless specifically prescribed for such use, as eberconazole may cause irritation in these sensitive areas.
- Eberconazole should be used with caution in individuals with liver dysfunction or a history of hepatic impairment, as the risk of hepatotoxicity may be increased (as highlighted in the research by Moodahadu-Bangera et al. in the Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology).
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult with a healthcare professional before using eberconazole, as the potential risks to the fetus or nursing infant have not been fully established.
Contraindications
Eberconazole should not be used in certain situations or by individuals with specific conditions, as it may pose a significant risk or exacerbate existing medical issues. Contraindications for eberconazole use include:
- Known hypersensitivity or allergy to eberconazole or any of its components, as this may increase the risk of severe allergic reactions.
- Concurrent use of potent cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors, such as ketoconazole or itraconazole, as these may significantly increase eberconazole levels in the body, potentially leading to toxicity (as discussed in the American Journal of Otolaryngology article by de la Paz Cota et al.).
- Individuals with severe hepatic impairment or active liver disease, as eberconazole may further compromise liver function and increase the risk of adverse hepatic effects.
It is crucial to disclose all medical conditions and medications to healthcare professionals to ensure the safe and appropriate use of eberconazole.
Interactions
Eberconazole may interact with certain medications, potentially altering their effectiveness or increasing the risk of adverse effects. It is crucial to inform healthcare professionals about all medications, supplements, and herbal products being taken to prevent potential interactions.
- Concomitant use of eberconazole with certain cytochrome P450 3A4 inhibitors, such as ketoconazole or itraconazole, may increase eberconazole levels in the body, potentially leading to toxicity (as discussed in the American Journal of Otolaryngology article by de la Paz Cota et al.).
- Eberconazole may interact with medications that undergo hepatic metabolism, as it has the potential to inhibit certain liver enzymes responsible for drug metabolism.
- Caution should be exercised when using eberconazole concurrently with other antifungal agents or medications that may cause liver toxicity, as the risk of hepatic adverse effects may be increased.
Overdose
In the event of an accidental or intentional overdose of eberconazole, prompt medical attention is crucial, as excessive levels of the drug may lead to adverse effects or toxicity.
- Symptoms of eberconazole overdose may include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dizziness, and liver dysfunction.
- Treatment for eberconazole overdose is primarily supportive, involving measures to manage any specific symptoms and monitor liver function.
- If eberconazole overdose is suspected, seek immediate medical assistance and provide healthcare professionals with accurate information about the amount ingested and the time of ingestion.
Additional Important Information
Development of Resistance
The widespread and indiscriminate use of antifungal agents, including eberconazole, has raised concerns about the potential development of resistance in fungal pathogens. To mitigate this risk, it is crucial to follow proper treatment guidelines and avoid unnecessary or inappropriate use of eberconazole.
Preclinical and Clinical Studies
Numerous preclinical and clinical investigations have been carried out to assess the pharmacological characteristics, safety, and effectiveness of eberconazole. One noteworthy study examined the possibility of ethyl cellulose microsponge gels loaded with eberconazole nitrate for topical fungal treatment. It was published in the journal Therapeutic Delivery by Bothiraja et al. The formulation’s potential to improve medication penetration and sustained release was investigated by the scientists, who found encouraging outcomes for better antifungal therapy.
While these studies offer insightful information, it is crucial to remember that each person’s reaction to eberconazole may differ, and constant supervision by medical specialists is advised during therapy.
Post-approval Studies, Pharmacovigilance and Pharmacokinetic Characteristics
Pharmacovigilance and post-marketing surveillance are essential for tracking eberconazole’s effectiveness and safety in actual clinical settings. The purpose of these investigations is to find possible side effects, medication interactions, and pharmacokinetic differences that might not have been discovered in the early stages of clinical trials. Gaining knowledge of eberconazole’s pharmacokinetic characteristics—such as its distribution, metabolism, absorption, and excretion—can help in dose optimisation and enhance patient outcomes.
Comparative Effectiveness
Clinical decision-making requires the use of comparative studies comparing the efficacy of eberconazole with other antifungal medications. In a study published in the American Journal of Otolaryngology, de la Paz Cota et al. contrasted the safety and effectiveness of clotrimazole 1% solution with eberconazole 1% otic solution in individuals with otomycosis. These head-to-head comparisons aid in the selection of treatments and assist comprehend the relative efficacy of eberconazole.
Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses combine information from several trials to offer a thorough assessment of the safety, effectiveness, and possible uses of eberconazole. These thorough assessments can point out areas that need more investigation, draw attention to any biases or limits in the body of current literature, and assist in the development of evidence-based therapy recommendations.
Current Research Directions and Future Perspectives
The goal of ongoing research is to investigate new eberconazole formulations, delivery methods, and therapeutic uses. An example of a new method to improve medication delivery and therapeutic efficacy is the work of Bothiraja et al. (Therapeutic Delivery), which examined the possibility of eberconazole nitrate-loaded ethyl cellulose microsponge gels for topical fungal treatment.
Moreover, the growing danger of resistance to antifungals emphasises the necessity of further investigation into the mechanisms of action of eberconazole and possible resistance patterns. To help overcome resistance and expand eberconazole’s therapeutic uses, researchers should consider investigating synergistic combinations with other antifungal drugs or discovering novel targets for the medication.
Future prospects for eberconazole may include broader indications, better formulations for targeted administration, and incorporation into multidisciplinary therapy methods for complicated fungal infections as scientific understanding and technical breakthroughs evolve.
Briefly
Eberconazole is a broad-spectrum antifungal agent belonging to the imidazole class of drugs. It demonstrates strong action against a variety of pathogenic fungi, such as opportunistic fungus, yeasts, and dermatophytes. The main way that eberconazole works is by preventing the manufacture of ergosterol, which is essential for the fungal cell membrane. This causes problems with the function of the cell membrane and ultimately results in the death of the cell.
Various superficial and mucocutaneous fungal infections, including tinea corporis, tinea cruris, tinea pedis, candidiasis, and others affecting the skin, nails, and mucous membranes, are the main conditions for which this drug is used topically. Although eberconazole is typically well tolerated, it can occasionally result in allergic responses or liver malfunction in addition to causing skin irritation and burning sensations.
Safe and effective usage requires taking the necessary measures, which include preventing damaged skin, monitoring for side effects, and avoiding medication interactions. Current studies address possible resistance issues and increase the clinical usefulness of eberconazole while investigating innovative formulations, delivery methods, and therapeutic uses.
ATTENTION: It is crucial never to take medication without a qualified doctor’s supervision. Always read the Patient Information Leaflet (PIL) with each prescribed medicine. Pharmaceutical companies accurately describe each product’s details, which may be regularly updated, though variations may exist depending on the drug’s composition. This article analyses the active ingredient rather than specific brand names containing this generic medicine worldwide. Study the instruction leaflet for each preparation you use. Close cooperation with your doctor and pharmacist is vital. Self-administering medication carries serious health risks and must be strictly avoided.
Bibliography
- LS Moodahadu-Bangera, J Martis, R Mittal… – Indian Journal of …, 2012 ijdvl
- BR de la Paz Cota, PPC Vega, JJM Navarrete… – American Journal of …, 2018 – Elsevier sciencedirect
- C Bothiraja, AD Gholap, KS Shaikh… – Therapeutic …, 2014 – Future Science future-science